- ALL
- CORPORATE
- BUSINESS
- OTHERS

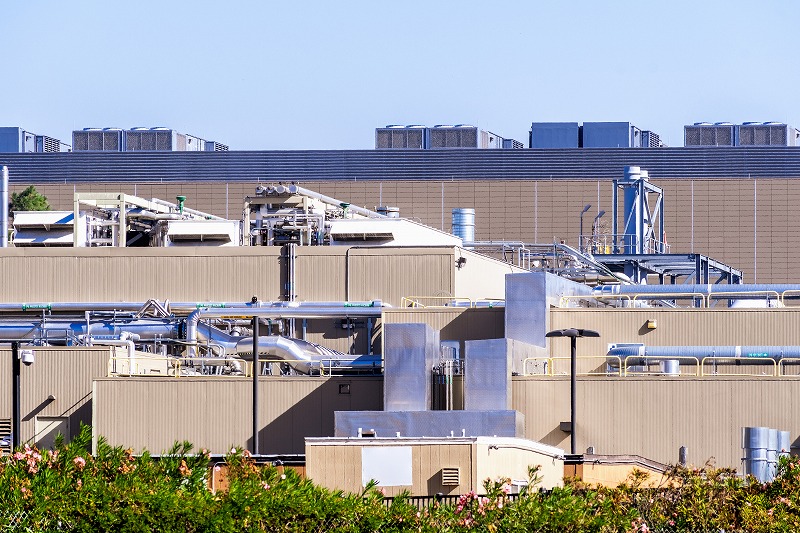
For a sustainable future for data centers and digital infrastructure
Data center investment in Japan is booming, and demand is expected to continue to grow. On the other hand, we are facing the warning about the enormous power consumption. In addition, most data centers are concentrated in Tokyo and Osaka, and it is still difficult to realize the national policy, i.e. "optimal arrangement of data centers in Japan". We Digital Infrastructure Lab are here to support a project to develop and utilize data centers and * digital infrastructure for the stakeholders auch as land owners, data center operators, developers, investors, energy operators, data center related equipment manufacturers, government, local governments.
* Not limited to data centers, it covers the fields of e-commerce logistics facilities, digital-related laboratories, base stations / communication networks, and renewable energy facilities.
To realize "ideal" digital infrastructure investment
- ALL
- TOPICS & NEWS
- Founder Message
- ESG + DC
2025.06.24
Watt-Bit Collaboration Opens New Horizons for Regional Revitalization: The Fusion of Energy and Digital Tech Driven by Technology and Policy
The Japanese government is now clearly emphasizing the importance of “Watt-Bit Collaboration”—the fusion of energy and digital technologies. The 2024 Basic Policy on Economic and Fiscal Management and Reform has positioned this collaboration as a core strategy, aiming to create a framework that simultaneously solves regional challenges and drives economic growth by integrally utilizing watts (electric power) and bits (digital data).
A key technology expected to drive this initiative is the next-generation decentralized ICT infrastructure known as IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network). By leveraging its decentralized and autonomous network architecture, IOWN enhances processing capabilities at the network’s edge. This structure allows for the distribution of massive power consumption and data processing to regional areas, rather than concentrating them in a few urban data centers. This capability makes it possible to overcome the limitations of over-concentration in metropolitan areas and establish a robust digital infrastructure in local communities.
The “Watt-Bit” Concept: A Vision That Thrives in Regional Japan
At its core, the Watt-Bit Collaboration is a vision designed for regional Japan, not a policy meant for metropolitan hubs like Tokyo and Osaka. This energy-x-digital approach is most effective when applied to the unique challenges plaguing rural areas, such as population decline and aging infrastructure. Today, advances in network technology—including fiber optics, 5G/Local 5G, and even satellite internet—have significantly overcome geographical disadvantages. An environment capable of handling advanced digital processing is rapidly taking shape in regional Japan.
From a power supply perspective, distributed data processing facilities also offer advantages to utility companies by providing greater flexibility for managing supply and demand and integrating renewable energy sources. In particular, a “locally-produced, locally-consumed digital infrastructure” that runs on renewable energy like solar and wind can enhance disaster preparedness and boost the overall resilience of local municipalities.
Will Big Tech Get on Board? The Next Challenge for Decentralized Infrastructure
However, this vision is not without its challenges. It remains uncertain whether global IT giants like GAFAM, which handle vast amounts of data, will embrace a decentralized regional infrastructure model. Their decisions will hinge on multiple factors, including the reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness of distributed edge computing and smaller-scale facilities. The ability to build an operational model that satisfies these global players will be the key to the nationwide success of the Watt-Bit Collaboration.
Moving forward, the initiative will require more than just national-level policy design and support. It calls for a diverse range of players—including local governments, private companies, power utilities, and telecommunication carriers—to work together to create a sustainable and practical model. The Watt-Bit Collaboration is not merely a technological endeavor; it is a national project that will define the very future of Japan’s regional communities.
2025.06.17
TEPCO Establishes New Digital Infrastructure Company Amid Data Boom
Tokyo Electric Power Company Power Grid (TEPCO PG) has established TEPCO Digital Infrastructure Co., Ltd. to advance its digital infrastructure business. This move comes against a backdrop of an explosion in data demand and the redefinition of power infrastructure driven by the widespread adoption of advanced digital technologies like generative AI. Power companies are no longer just energy suppliers; they’re evolving into crucial partners underpinning our data-driven society.
A prime example of this evolution is the joint data center development in the Inzai-Shiroi area of Chiba Prefecture by NTT Data Group, NTT Global Data Centers, and TEPCO PG. Announced in late 2023, this plan involves establishing a Special Purpose Company (SPC) within fiscal year 2023, with services aiming to launch in the latter half of 2026. The initial phase will see the construction of a large-scale data center with 50 MW of power capacity for IT equipment, with further joint developments progressively being considered, primarily in the Tokyo metropolitan area.
The Fusion of Power Company Expertise and ICT Company Technology
The significance of this project lies in the synergy between TEPCO PG’s extensive asset base and power operation expertise, and the NTT Group’s advanced ICT technologies and global data center operational capabilities. Together, they aim to build a more sophisticated and sustainable data center model. This design philosophy, particularly its ability to address societal challenges like decarbonization and distributed power sources, points toward the future direction of next-generation infrastructure.
Similar initiatives are emerging from other power companies. Tohoku Electric Power, for instance, has launched a new business for generative AI using containerized mobile data centers. A key feature of this initiative is its speed-to-market approach, enabling GPU-equipped servers to be operational within a few months. Spearheaded by ideas from younger and mid-career employees, this project leverages the cool climate of the Tohoku region for efficient power consumption and also lays the groundwork for attracting large-scale data centers in the future.
“Electricity’s” Growing Presence as the Foundation of the Data Society
Underlying these developments is a structural shift in electricity demand. With the establishment and expansion of data centers and semiconductor factories, peak electricity demand is projected to reach 7.15 million kilowatts by 2034. This makes redesigning Japan’s electricity supply system an urgent priority. Addressing challenges such as stable supply, renewable energy integration, and securing baseload power simultaneously necessitates an integrated approach between electricity and digital infrastructure.
As power companies become deeply involved in digital infrastructure, data centers and electricity have become inextricably linked. High-density, always-on digital foundations demand vast and stable power supplies. Conversely, for power companies, data centers represent the most realistic growth driver as they seek decarbonization and new revenue streams.
In essence, power companies and data center operators are now transcending the traditional supplier-user relationship, transforming into partners jointly building the social infrastructure. To envision a future that balances both stable supply and sustainability, it is absolutely essential for both parties to team up and tackle these challenges together.
2025.05.27
Tsukuba’s 1GW Project Signals the Dawn of the Mega Data Center Era
The trend towards increasingly large-scale data centers (DCs) is gaining serious traction, highlighted by Tsukuba’s first hyperscale data center project, which drew significant attention during its bidding phase. This initiative is spearheaded by Australia’s Goodman Group. In 2022, the company successfully acquired approximately 45 hectares of land in response to a public call for proposals conducted by Tsukuba City as part of its industrial promotion strategy. This region, developed as a “Science City,” already possesses well-established infrastructure, including telecommunications, power, and water, along with excellent accessibility from the Tokyo metropolitan area. Furthermore, it offers significant potential for further development, making it one of the few locations in Japan equipped to host hyperscale data centers.
The Full Scope of the 1GW Hyperscale DC Development
In January 2024, Goodman formally announced the “Goodman Tsukuba Data Center Campus.” The vision is for a campus-style data center envisioned to have a maximum power capacity of up to 1GW (1000MW) – a scale unprecedented in Japan. The first phase, a 50MW facility, is currently under construction and slated for completion in 2026. Notably, preliminary agreements with key anchor tenants are already in place, highlighting its alignment with current market demand. Goodman also operates a data center cluster exceeding 300MW in Inzai City, Chiba, and Tsukuba is set to become its next flagship location.
Next-Generation Infrastructure Driven by Global Strategy and Environmental Commitment
Goodman’s data center strategy is global, with developments also underway in other key global cities such as Hong Kong, Los Angeles, Sydney, and Melbourne. In February 2025, Goodman announced it had secured approximately USD 4 billion (around JPY 600 billion) for data center development. The company is projecting up to USD 80 billion in development opportunities over the next 5 to 7 years and has already secured a total power capacity of 4GW.
The company is also at the forefront of environmental sustainability. Through low-carbon building design and the proactive integration of renewable energy, Goodman is strengthening its adherence to ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria. This is a significant draw for global cloud providers and AI operators that prioritize sustainability.
A Project Redefining Japan’s Role in the Mega Data Center Era
Thus, the 1GW-class data center development in Tsukuba stands as a landmark project, heralding a new phase for Japan’s domestic data center industry. This plan, achieved through a collaboration between public and private sectors, not only enhances the value of the region but is also garnering considerable attention as an initiative poised to redefine Japan’s standing in the age of mega data centers.
2025.05.26
Here is the English translation of the blog post: Former Prestigious Factory Sites Transform into IT Hubs: Accelerating Data Center Redevelopment
Large factories once supporting Japan’s rapid economic growth, such as steelworks and electronics manufacturers, are now successively transforming into data centers (DCs) in response to the demands of the digital age. A prominent example drawing attention is the DC project in Kawasaki City by Mitsubishi Corporation and JFE Holdings.
Former Manufacturing Bases Evolve into the Heart of the AI Era
The two companies are moving forward with a plan to invest 100 to 150 billion yen to construct a large-scale data center on the site of the JFE Steel East Japan Works Keihin District (Kawasaki coastal area), where blast furnace operations ceased in 2023. A feasibility study is slated for completion by fiscal year 2025, with operations scheduled to begin as early as fiscal year 2030. If realized, it will be the largest DC operated by the Mitsubishi Corporation Group, with an anticipated power consumption of 60,000 to 90,000 kilowatts.
This plan reflects a symbolic paradigm shift from manufacturing to information industries. The Kawasaki steelworks was a crucial base that supported Japan’s steel industry for approximately 90 years, dating back to the Japan Steel Tube era. However, intense global competition led to the cessation of blast furnace operations. Now, this very site is set to transform into a state-of-the-art information infrastructure that meets the demands of AI and cloud computing.
In particular, the widespread adoption of generative AI has rapidly increased the need for infrastructure capable of high-speed processing of large volumes of data. Demand for servers using high-performance semiconductors from US-based Nvidia is also rising, prompting companies to seek new DC locations. Former factory sites, with their expansive land and robust power infrastructure, offer ideal conditions to meet these requirements.
Sakai, Kawasaki, and Across Japan: Redefining Former Factory Sites
Similar movements are becoming evident in other regions. In Sakai City, Osaka Prefecture, the Sakai Factory, known for Sharp’s LCD panel manufacturing, is undergoing a transformation plan to become a DC under the hands of major telecommunications companies SoftBank and KDDI. What was once a “monozukuri (manufacturing) hub” is now poised to evolve into an “information processing hub.”
According to forecasts by research firm Fuji Keizai, Japan’s domestic DC market is expected to reach 5,403.6 billion yen in 2029, a 34% increase compared to 2024. Consequently, not only traditional office buildings and suburban facilities, but also industrial zones in urban peripheries are gaining attention as DC locations.
The repurposing of industrial land is a topic that concerns not only real estate development but also energy policy and regional revitalization. Data centers, in particular, consume massive amounts of electricity, making the introduction of renewable energy and the establishment of local production and consumption power supply systems key for the future.
Factory complexes that once drove the Japanese economy are once again in the spotlight as foundational infrastructure for the digital society. From heavy industries to information industries—the demands of the times and technological evolution are fundamentally reshaping urban landscapes and land values.
2023.07.05
Google warns Irish government moratorium on data center development
Irish government restricts data center development
Ireland’s The Commission for Regulation of Utilities (CRU) has decided to limit the impact by imposing a de facto moratorium on new data center development in the Dublin metropolitan area.
Ireland’s national transmission operator EirGrid said in response that it would only consider new applications for grid connection on a case-by-case basis. The restrictions could reportedly last until 2028.
Martin Shanahan, CEO of Ireland’s Industrial Development Authority (IDA), recently said that new data centers “are unlikely to occur in Dublin and the East Coast at this time.”
Google has asked such Irish regulators not to impose a moratorium on data center development in the country.
In The Commission for Regulation of Utilities (CRU) filing, the company said search and cloud companies must “absolutely” avoid a moratorium on data center development.
Google said such a ban would send a “wrong signal” about Ireland’s digital economy ambitions, and would affect the country’s infrastructure, according to a Freedom of Information request first reported by The Irish Times. It adds that it makes further investment “impossible”.
In the filing, Google called for more transparency about where the Irish network has existing power capacity, as well as being clearer and more open about EirGrid’s projections of data center power usage growth. I think you need to.
Growing Demand for Cloud Computing, Google’s Proposal
Google, which launched its first data center in Ireland in 2012, has proposed a new pricing structure for data center operators who reserve more capacity than they ultimately need or grow to that capacity too slowly. bottom.
“Transmission tariffs can be designed so that consumers who are not seeing increased demand towards maximum reserved capacity will be charged more than consumers who are demonstrating an increase each year.” says.
EirGrid and politicians have previously suggested moving data center development to the west of Ireland (away from Dublin’s constrained areas and closer to renewable energy sources), but Google says this is not a viable solution. I point out that it is not.
“The demand for cloud computing in Dublin is growing. We are unable to provide services.”
Another AWS filing says Ireland has missed opportunities in the past to address supply issues.
“Over the past decade, we have had opportunities to do reinforcement work, prepare the grid for growth and investment, and prepare the grid for more intermittent integration of resources,” he said.
Both the Social Democrats and the People Before Profit parties have been calling for a nationwide moratorium on future data center projects for the past 12 months. The PBP bill was an absolute ban on data centers, liquid natural gas plants and new fossil fuel infrastructure.
In Dublin last month, South Dublin County Council (SDCC) voted to block future data center construction in the county as part of a new development plan.
What is the background behind the Irish government’s moratorium on data center development?
Irish Government Behind Data Center Development Moratorium
The Irish government’s achievement of emissions and renewable energy targets is behind this.
According to EirGrid, data center energy usage is projected to increase by 9TWh by 2030, ranging from 23% to 31% of Ireland’s grid supply in 2030. This comes at a time when the government wants to reduce emissions by 60-80% by increasing the share of renewable energy. At the same time, governments want to decarbonise by moving heating and transportation to electricity, further increasing demand on the grid.
According to The Irish Times, EirGrid has agreed to connect an additional 1.8GW of data centers to the grid, with current peak demand of around 5GW, and a further 2GW of applications ready. That’s it.
The Government Statement on the Role of Data Centers in Ireland’s Enterprise Strategy 2018, published in 2018, emphasized the positive role of data centers in the country’s economic performance. However, it will now be “aligned with sectoral emissions caps and renewable energy targets, concerns about continued security of supply, and demand flexibility measures currently needed. In order to secure it, it will be reviewed. “In addition, further tightening of regulations will be considered,” it is reported.
Will it work or will it backfire?
The Irish government imposes a moratorium on data center development, which is in high demand worldwide. It seems that the moratorium continues while receiving a warning from Google. Will this decision work or will it backfire? We will keep an eye on trends.
2023.03.26
Data center facility inspection robots to be fully deployed from April 2023 (NTT DATA)
NTT DATA Co., Ltd. is working to remote/automate equipment inspection work using robots at the data center “NTT Shinagawa TWINS DATA Building” (hereinafter referred to as “Shinagawa Data Center”) operated by the company. announced that it has confirmed that it is possible to reduce the equipment inspection work that was previously done by about 50%.
From April 2023, NTT DATA will proceed with the introduction of robots to data centers nationwide.
Background of robot introduction
NTT DATA explained that the building management industry, including data centers, is facing a serious manpower shortage, and that facility management work, in particular, is facing a shortage of skilled workers, and that there is a need for labor savings and more efficient work implementation.
Among facility management operations, the company believes that inspection work is highly effective in reducing manpower and that remote/automated operations are feasible through the use of digital technology, and has been conducting verification for practical application at its Shinagawa Data Center.
Overview of Robot Introduction and Changing Checking Tasks
In this initiative, a robot automatically patrols a predetermined inspection route, taking pictures of meters, lamps, and facility exterior, and acquiring environmental data such as odors using sensors, thereby replacing the work of measuring meters, checking lamps, and checking for abnormalities in appearance and unusual odors that had previously been performed by humans.
In this method, a single camera or sensor can be used to inspect multiple locations, and there is no need to modify the current equipment in operation, making it cheaper and simpler to achieve remote/automated operation than other methods such as installing IoT cameras and sensors for each inspection target or converting to smart meters.
The robot used in this project is a next-generation avatar robot “ugo Pro” modified for facility inspection work in collaboration with ugo Corporation, a manufacturer of business DX robots.
In order to capture detailed meter readings, the robot is equipped with a 4K camera with higher image quality than the standard model, and multiple devices such as an odor sensor, microphone, and thermo camera can be mounted on the ugo itself to expand its applications depending on the inspection items.
The robot can be operated using only a PC, and its travel route can be set with no code, making it easy for on-site personnel to use the robot. The robot can switch between automatic traveling and remote control, and can be used not only for automatic inspection work, but also for multiple applications, such as work support from a distance.
These features not only allow the robot to handle a variety of inspection items, but also to expand its applications to include remote work support and construction attendance.
By using robots and sensors to remotely/automatically perform inspection work, not only can work hours be reduced, but also the threshold values for determining abnormalities, which used to rely on human senses, can be quantified to enable detection of abnormalities without relying on skilled workers.
In addition, by making it possible to remotely perform tasks that could only be performed onsite, including work support and construction attendance, it is expected to support flexible work styles and secure new workers.
About the future
In the future, NTT DATA aims to expand the scope of automation to include recording and reporting work that currently requires personnel to perform, and to reduce the time required for inspection work by up to 80% by promoting linkage with meter reading systems and abnormality detection AI.
NTT Data will also work to enhance facility management operations, such as advanced abnormality detection and predictive maintenance of facilities, utilizing data acquired by robots and sensors.
Starting in April 2023, the initiative will be rolled out sequentially to 15 data centers nationwide.
Furthermore, based on the knowledge gained from these efforts, the company aims to offer the service commercially as a remote/automated service for facility inspection operations by the end of FY2023.
For commercial provision, ugo will utilize the new robot “ugo mini” developed by making use of the knowledge obtained through joint verification with NTT DATA to develop remote/automation solutions for facility management operations, from consulting for introduction. NTT DATA provide one-stop support from system construction to operation to solve customer problems.
The day of full-scale deployment of robots for facility inspection operations at data centers is eagerly awaited to help resolve the serious labor shortage.
2023.03.11
Announced the start of construction of “Zero Emission Data Center” planned in Ishikari City, Hokkaido (KCCS)
On November 24, 2022, Kyocera Communication Systems Corporation (KCCS) announced that KCCS will begin construction of a zero-emission data center in Ishikari City, Hokkaido, Japan, in December 2022, with the data center scheduled to open in the fall of 2024.
In 2019, KCCS announced plans for a zero-emission data center in Ishikari, Hokkaido, which will operate on 100% renewable energy.
Subsequently, due to a change in the originally planned baseload power supply plan, the power supply configuration and data center design were revised, and now the company has announced the start of construction and opening schedule.
The data center to be constructed will be located in the Ishikari Bay New Port area of Ishikari City, Hokkaido, with a site area of approximately 15,000 square meters, total floor space of approximately 5,300 square meters (at the time of opening), and 400 racks (at the time of opening).
Toward Achieving Carbon Neutrality by 2050
In Japan, local production and local consumption of renewable energy is an important theme for achieving carbon neutrality (virtually zero greenhouse gas emissions) by 2050, as is the decentralization of data centers in the “Digital Rural City State Concept” being promoted by the government. The introduction of “real renewable energy,” which reduces environmental impact to plus or minus zero through the purchase of environmental values such as non-fossil certificates, is progressing.
To this end, expansion of “direct use of renewable energy” is also needed to further increase the amount of renewable energy introduced.
However, it is not easy to achieve “direct use of renewable energy” in large-scale demand facilities such as data centers, as securing stable renewable energy power and economic efficiency is a challenge.
Ishikari City has been selected as a “Decarbonization Leading Region (1st round)” by the Ministry of the Environment in a publicly solicited project to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
In addition, KCCS has formulated the “Redesigning the Region through Local Production of Renewable Energy and Decarbonization,” a measure aimed at zero carbon, and is aiming for a decarbonized industrial cluster by supplying renewable energy to the data center cluster and surrounding facilities in the Ishikari Bay New Port area.
The zero-emission data center will utilize the abundant renewable energy sources in the region, and a new solar power plant owned by KCCS will be built in the vicinity of the data center to directly utilize those renewable energy sources.
In addition, in order to operate the data center while simultaneously ensuring the “reliability,” “environmental friendliness,” and “economic efficiency” of multiple renewable energy sources, KCCS will build its own power supply and demand control mechanism utilizing storage batteries and AI technology.
KCCS aims to demonstrate the possibility of local production for local consumption of renewable energy through the “data center business operated on 100% renewable energy” in Ishikari City, as well as to contribute to regional revitalization through decentralized data storage in Japan and the creation of jobs for data center technicians and energy-related engineers. The project also aims to contribute to regional revitalization by creating jobs for data center technicians and energy-related engineers.
Expectations are high for the opening of a “zero-emission data center” to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
2023.03.01
Commitment to be water positive by 2030 (AWS)
What is Water Positive
Water positive means providing more water than you consume. With freshwater shortages becoming an issue around the world, companies are making various efforts to secure water.
There are two main ways to do it: either reduce consumption or increase supply.
There are ways to reduce water consumption, such as water conservation and recycling, and ways to increase water supply, such as investing in areas and businesses with high water stress, such as water scarcity and water pollution.
AWS Committed to Reducing Water Use in Data Centers
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the new hyperscaler that has committed to making their business water positive.
At the AWS re:Invent event held in Las Vegas, the company announced a policy to achieve water positive by 2030, returning more water to the community than it uses directly in its operations.
AWS CEO Adam Selipsky said:
“Water scarcity is a major problem around the world, and with today’s announcement by Water Positive, we are committed to doing our part to help solve this fast-growing problem.
To ensure universal access to water, we need to develop new ways to conserve and reuse this precious resource. While we are proud of what we have achieved so far, we also believe that more can be done.
We are committed to leading water stewardship in our cloud business and giving back more water than we use in the communities in which we operate. We believe this is the right thing to do for the environment and our customers. ”
The company’s efforts to achieve this goal include: analyzing water usage in real time, using IoT technology to identify and fix leaks, using recycled or rainwater for cooling, and reusing water multiple times. It includes replenishment as well as reimbursement activities, including the availability of on-site water treatment systems, and where possible, funding for waterless cooling and various water replenishment activities at the facility.
In 2021, AWS said it achieved a global Water Use Efficiency (WUE) index of 0.25L water per kWh. In Ireland and Sweden, AWS says it doesn’t use water to cool its data centers 95% of the year.
According to a US Department of Energy report, the average evaporative cooling data center WUE is 1.8L per kWh.
In the UK, AWS is working with The Rivers Trust and Action for the River Kennet to create two wetlands on tributaries of the River Thames.
“England’s rivers are national treasures and we are delighted to partner with AWS and work with our member trusts here to protect the Thames and its tributaries,” said Mark Lloyd, CEO of The Rivers Trust. said.
“AWS’ commitment to be water positive by 2030 drives the actions needed to help restore rivers and water resources impacted by climate change.
We look forward to expanding our relationship with AWS and using this partnership to demonstrate similar avenues for other companies to jointly support water management activities that improve the resilience of rivers. ”
Data centers use a lot of water for cooling, but it’s not clear how much water the industry actually uses.
Researchers estimate that on average in the US, 1 MWh of data center energy consumption requires 7.1 cubic meters of water, but this can vary widely by region and facility.
Efforts of Google, Microsoft and Meta
Google, Meta and Microsoft have committed to being water positive by 2030, but many of their facilities now use millions of gallons of water per day.
Colocation and peering service provider CyrusOne, which owns and operates over 40 carrier-neutral data centers in North America, Europe and South America, claims several of its facilities are water positive.
Morningstar Sustainalytics, a leading ESG research, ratings, and data provider that has helped investors around the world develop and implement responsible investment strategies, previously released a report showing that Microsoft is leading the market in water conservation efforts.
European data center operators pledged to the European Commission earlier this year to reduce water usage to up to 400ml per kWh of computer power by 2040.
Due to the effects of global warming and population growth, water shortages are becoming a problem around the world. We will continue to keep an eye on the water positive initiatives of major companies.
2022.09.05
2022.09.05
2022.09.05
2022.09.05
2025.06.24
Watt-Bit Collaboration Opens New Horizons for Regional Revitalization: The Fusion of Energy and Digital Tech Driven by Technology and Policy
The Japanese government is now clearly emphasizing the importance of “Watt-Bit Collaboration”—the fusion of energy and digital technologies. The 2024 Basic Policy on Economic and Fiscal Management and Reform has positioned this collaboration as a core strategy, aiming to create a framework that simultaneously solves regional challenges and drives economic growth by integrally utilizing watts (electric power) and bits (digital data).
A key technology expected to drive this initiative is the next-generation decentralized ICT infrastructure known as IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network). By leveraging its decentralized and autonomous network architecture, IOWN enhances processing capabilities at the network’s edge. This structure allows for the distribution of massive power consumption and data processing to regional areas, rather than concentrating them in a few urban data centers. This capability makes it possible to overcome the limitations of over-concentration in metropolitan areas and establish a robust digital infrastructure in local communities.
The “Watt-Bit” Concept: A Vision That Thrives in Regional Japan
At its core, the Watt-Bit Collaboration is a vision designed for regional Japan, not a policy meant for metropolitan hubs like Tokyo and Osaka. This energy-x-digital approach is most effective when applied to the unique challenges plaguing rural areas, such as population decline and aging infrastructure. Today, advances in network technology—including fiber optics, 5G/Local 5G, and even satellite internet—have significantly overcome geographical disadvantages. An environment capable of handling advanced digital processing is rapidly taking shape in regional Japan.
From a power supply perspective, distributed data processing facilities also offer advantages to utility companies by providing greater flexibility for managing supply and demand and integrating renewable energy sources. In particular, a “locally-produced, locally-consumed digital infrastructure” that runs on renewable energy like solar and wind can enhance disaster preparedness and boost the overall resilience of local municipalities.
Will Big Tech Get on Board? The Next Challenge for Decentralized Infrastructure
However, this vision is not without its challenges. It remains uncertain whether global IT giants like GAFAM, which handle vast amounts of data, will embrace a decentralized regional infrastructure model. Their decisions will hinge on multiple factors, including the reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness of distributed edge computing and smaller-scale facilities. The ability to build an operational model that satisfies these global players will be the key to the nationwide success of the Watt-Bit Collaboration.
Moving forward, the initiative will require more than just national-level policy design and support. It calls for a diverse range of players—including local governments, private companies, power utilities, and telecommunication carriers—to work together to create a sustainable and practical model. The Watt-Bit Collaboration is not merely a technological endeavor; it is a national project that will define the very future of Japan’s regional communities.
2025.06.17
TEPCO Establishes New Digital Infrastructure Company Amid Data Boom
Tokyo Electric Power Company Power Grid (TEPCO PG) has established TEPCO Digital Infrastructure Co., Ltd. to advance its digital infrastructure business. This move comes against a backdrop of an explosion in data demand and the redefinition of power infrastructure driven by the widespread adoption of advanced digital technologies like generative AI. Power companies are no longer just energy suppliers; they’re evolving into crucial partners underpinning our data-driven society.
A prime example of this evolution is the joint data center development in the Inzai-Shiroi area of Chiba Prefecture by NTT Data Group, NTT Global Data Centers, and TEPCO PG. Announced in late 2023, this plan involves establishing a Special Purpose Company (SPC) within fiscal year 2023, with services aiming to launch in the latter half of 2026. The initial phase will see the construction of a large-scale data center with 50 MW of power capacity for IT equipment, with further joint developments progressively being considered, primarily in the Tokyo metropolitan area.
The Fusion of Power Company Expertise and ICT Company Technology
The significance of this project lies in the synergy between TEPCO PG’s extensive asset base and power operation expertise, and the NTT Group’s advanced ICT technologies and global data center operational capabilities. Together, they aim to build a more sophisticated and sustainable data center model. This design philosophy, particularly its ability to address societal challenges like decarbonization and distributed power sources, points toward the future direction of next-generation infrastructure.
Similar initiatives are emerging from other power companies. Tohoku Electric Power, for instance, has launched a new business for generative AI using containerized mobile data centers. A key feature of this initiative is its speed-to-market approach, enabling GPU-equipped servers to be operational within a few months. Spearheaded by ideas from younger and mid-career employees, this project leverages the cool climate of the Tohoku region for efficient power consumption and also lays the groundwork for attracting large-scale data centers in the future.
“Electricity’s” Growing Presence as the Foundation of the Data Society
Underlying these developments is a structural shift in electricity demand. With the establishment and expansion of data centers and semiconductor factories, peak electricity demand is projected to reach 7.15 million kilowatts by 2034. This makes redesigning Japan’s electricity supply system an urgent priority. Addressing challenges such as stable supply, renewable energy integration, and securing baseload power simultaneously necessitates an integrated approach between electricity and digital infrastructure.
As power companies become deeply involved in digital infrastructure, data centers and electricity have become inextricably linked. High-density, always-on digital foundations demand vast and stable power supplies. Conversely, for power companies, data centers represent the most realistic growth driver as they seek decarbonization and new revenue streams.
In essence, power companies and data center operators are now transcending the traditional supplier-user relationship, transforming into partners jointly building the social infrastructure. To envision a future that balances both stable supply and sustainability, it is absolutely essential for both parties to team up and tackle these challenges together.
2025.05.27
Tsukuba’s 1GW Project Signals the Dawn of the Mega Data Center Era
The trend towards increasingly large-scale data centers (DCs) is gaining serious traction, highlighted by Tsukuba’s first hyperscale data center project, which drew significant attention during its bidding phase. This initiative is spearheaded by Australia’s Goodman Group. In 2022, the company successfully acquired approximately 45 hectares of land in response to a public call for proposals conducted by Tsukuba City as part of its industrial promotion strategy. This region, developed as a “Science City,” already possesses well-established infrastructure, including telecommunications, power, and water, along with excellent accessibility from the Tokyo metropolitan area. Furthermore, it offers significant potential for further development, making it one of the few locations in Japan equipped to host hyperscale data centers.
The Full Scope of the 1GW Hyperscale DC Development
In January 2024, Goodman formally announced the “Goodman Tsukuba Data Center Campus.” The vision is for a campus-style data center envisioned to have a maximum power capacity of up to 1GW (1000MW) – a scale unprecedented in Japan. The first phase, a 50MW facility, is currently under construction and slated for completion in 2026. Notably, preliminary agreements with key anchor tenants are already in place, highlighting its alignment with current market demand. Goodman also operates a data center cluster exceeding 300MW in Inzai City, Chiba, and Tsukuba is set to become its next flagship location.
Next-Generation Infrastructure Driven by Global Strategy and Environmental Commitment
Goodman’s data center strategy is global, with developments also underway in other key global cities such as Hong Kong, Los Angeles, Sydney, and Melbourne. In February 2025, Goodman announced it had secured approximately USD 4 billion (around JPY 600 billion) for data center development. The company is projecting up to USD 80 billion in development opportunities over the next 5 to 7 years and has already secured a total power capacity of 4GW.
The company is also at the forefront of environmental sustainability. Through low-carbon building design and the proactive integration of renewable energy, Goodman is strengthening its adherence to ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria. This is a significant draw for global cloud providers and AI operators that prioritize sustainability.
A Project Redefining Japan’s Role in the Mega Data Center Era
Thus, the 1GW-class data center development in Tsukuba stands as a landmark project, heralding a new phase for Japan’s domestic data center industry. This plan, achieved through a collaboration between public and private sectors, not only enhances the value of the region but is also garnering considerable attention as an initiative poised to redefine Japan’s standing in the age of mega data centers.
2025.05.26
Here is the English translation of the blog post: Former Prestigious Factory Sites Transform into IT Hubs: Accelerating Data Center Redevelopment
Large factories once supporting Japan’s rapid economic growth, such as steelworks and electronics manufacturers, are now successively transforming into data centers (DCs) in response to the demands of the digital age. A prominent example drawing attention is the DC project in Kawasaki City by Mitsubishi Corporation and JFE Holdings.
Former Manufacturing Bases Evolve into the Heart of the AI Era
The two companies are moving forward with a plan to invest 100 to 150 billion yen to construct a large-scale data center on the site of the JFE Steel East Japan Works Keihin District (Kawasaki coastal area), where blast furnace operations ceased in 2023. A feasibility study is slated for completion by fiscal year 2025, with operations scheduled to begin as early as fiscal year 2030. If realized, it will be the largest DC operated by the Mitsubishi Corporation Group, with an anticipated power consumption of 60,000 to 90,000 kilowatts.
This plan reflects a symbolic paradigm shift from manufacturing to information industries. The Kawasaki steelworks was a crucial base that supported Japan’s steel industry for approximately 90 years, dating back to the Japan Steel Tube era. However, intense global competition led to the cessation of blast furnace operations. Now, this very site is set to transform into a state-of-the-art information infrastructure that meets the demands of AI and cloud computing.
In particular, the widespread adoption of generative AI has rapidly increased the need for infrastructure capable of high-speed processing of large volumes of data. Demand for servers using high-performance semiconductors from US-based Nvidia is also rising, prompting companies to seek new DC locations. Former factory sites, with their expansive land and robust power infrastructure, offer ideal conditions to meet these requirements.
Sakai, Kawasaki, and Across Japan: Redefining Former Factory Sites
Similar movements are becoming evident in other regions. In Sakai City, Osaka Prefecture, the Sakai Factory, known for Sharp’s LCD panel manufacturing, is undergoing a transformation plan to become a DC under the hands of major telecommunications companies SoftBank and KDDI. What was once a “monozukuri (manufacturing) hub” is now poised to evolve into an “information processing hub.”
According to forecasts by research firm Fuji Keizai, Japan’s domestic DC market is expected to reach 5,403.6 billion yen in 2029, a 34% increase compared to 2024. Consequently, not only traditional office buildings and suburban facilities, but also industrial zones in urban peripheries are gaining attention as DC locations.
The repurposing of industrial land is a topic that concerns not only real estate development but also energy policy and regional revitalization. Data centers, in particular, consume massive amounts of electricity, making the introduction of renewable energy and the establishment of local production and consumption power supply systems key for the future.
Factory complexes that once drove the Japanese economy are once again in the spotlight as foundational infrastructure for the digital society. From heavy industries to information industries—the demands of the times and technological evolution are fundamentally reshaping urban landscapes and land values.



 JA
JA











